Explain Different Routes of Medicine Administration
Transdermal a patch on the skin. The three main parenteral routes of drug administration are IV IM and SC and in all cases administration is usually via a hollow needle.
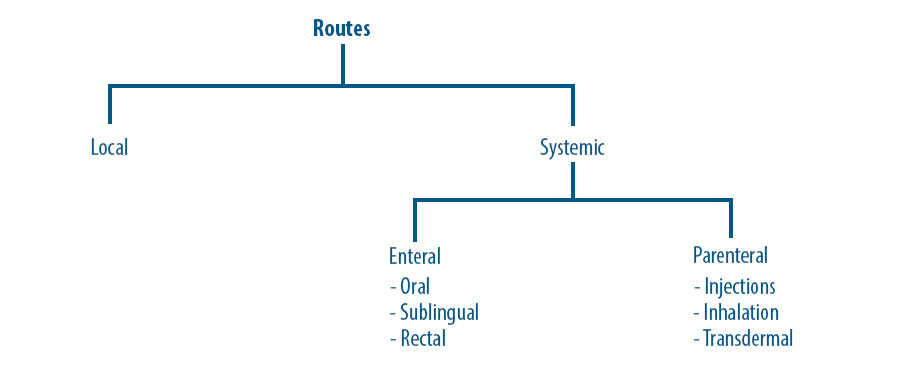
Routes Of Drug Administration An Overview Pharmapproach Com
32 Explain the different routes of medicine administration.

. Parenteral Route of Administration and Dosage Forms. To get a better understanding here are the 6 most common routes. Explain the different routes of medicine administration For example intravenous IV furosemide administered too quickly can cause deafness.
Rectal This may be the next option for those who cant swallow the medication. A drug given parenterally is one given by a route other than the mouth topical dosage forms are considered separately. 41 Explain the importance of the appropriate timing of medication.
Oral by mouth and swallow. Orally administered drugs absorbed mainly from small intestine. Via skin eyes ears nose vagina rectum lungs inhaled Parenteral.
Medication and their uses. Intra-ocular via the eyes. 33 Describe the common adverse reactions to medication and the appropriate actions required in line with agreed ways of working.
Pros Cons of Different Routes of Drug Administration 1. The drug is administered rectally as a suppository. Corticosteroids may be injected by this route in acute arthritis.
Inhaled through the mouth or nose. 24 Explain the different routes of medicine administration 3 Understand procedures and techniques for the administration of medication 31 Explain the types purpose and function of materials and equipment needed for the administration of medication via the different routes. Sublingual underneath the tongue.
Intra-articular route involves injection into the joint cavity. Please explain the different routes of medication administration and which one is the fastest entry to the bloodstream. Make sure that the individual is in an upright and sitting position.
Over-application of topical steroids will cause thinning of the skin and may lead to systemic side-effects. Many individuals can only swallow one pill at a time. Intra-aural via the ears.
Explain the different routes of medicine administration Routes of administration are usually classified by application location or exposition. Routes of medication administration There are several different ways drugs can be. Unsuitable for those who are experiencing severe vomiting or have difficultyswallowingAlso.
Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. 24 Explain the different routes of medication administration. The oral route is the most frequently used route of medicines administration and is the most convenient and.
4 Be able to prepare for the administration of medication. Explain the buccalsublingual routes of administration. Routes of Medication Administration When giving medications by mouth such as pills or liquids there are some basic things to remember.
Be careful to give. Buccal by the buccal cavity. Topical on the skin.
These routes need to be Clinical Practice Review Box 1. Oral penicillin V given with food will not be well absorbed. Intraperitoneal route may be used for peritoneal dialysis.
Drug administration by mouth and tube feeding using nasogastric gastrostomy and jejunostomy tubes. Routes of administration There are various routes of administration Box crushed or broken1 each of which has advantages and disadvantages. When you take drugs by mouth and drug is absorbed from the GI tract.
Oral Swallowed through the patients mouth as either a tablet liquid capsule lozenge or chewable tablet. Penicillin may be injected in cases of lung empyma by intrapleural route. Little absorption occur in stomach because of small area and short residence time.
Intra nasal via the nose. Never give pills or liquids to an individual lying down. Administration routes Enteraloral via enteral feeding tubes Topical.
The sublingual route of administration is the medication placed under the tongue. Slow-release medications may extend the duration of the effect. The route or course the active substance takes from application location to the location where it has its target effect is usually rather a matter of pharmacokinetics.
Please explain the different routes of medication administration and which one is the fastest entry to the bloodstream. Start studying Routes of Administration. Medications are formulated to avoid stomach acids and digestive enzymes.
Via skin eyes ears nose vagina rectum lungs inhaled.

Comparison Of Three Different Routes Of Drug Administration Oral Download Scientific Diagram

Advantages And Disadvantages Of Different Routes Of Administration For Download Table
Comments
Post a Comment