What Makes an Amino Acid Unique
Removing a cofactor Extreme temperature Adding a competitive inhibitor Adding an allosteric. Therefore possession of a R side chain.

Pin On Nutrition Articles By Cen
The elements present in every amino acid are carbon C hydrogen H oxygen O and nitrogen N CHON.

. Question 15 1 pts What makes each amino acid unique. Amino acid sequence C. The long strands of glucose molecules.
In addition sulfur S is present in the side chains of cysteine and methionine and selenium Se. There are 20 different amino acids found in. Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and a carboxyl group are.
Each amino acid has 4 different groups attached to α- carbon. For example alanine leucine and phenylalanine are all non-polar hydrophobic amino acids. Amino acids are organic compounds that contain amino NH 3 and carboxylate CO 2 functional groups along with a side chain R group specific to each amino acid.
The amino group B. Each molecule contains a central carbon C atom called the α-carbon to which both an amino and a carboxyl group are attached. The carboxyl group C.
Primary structure is linear and link is maintained by a peptide bond. Look up for Quick Answers Now. Discover all the Benefits that you might get.
The R group D. There are 20 naturally occurring amino acids and all have common structural features an amino group -NH3 a carboxylate -COO- group and a hydrogen-bonded to the same carbon atom. They all have a common amine and carboxyl group but the 20 amino acids have variable R group which makes them specific and how they will interact with other amino acids.
All of their R groups are composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen. Each amino acid have different R group. The R group or side chain is unique to each amino acids.
Some proteins function as enzymes some as antibodies while others provide structural support. It have the amine group a carbon atom a hydrogen atom carboxyl group and an. Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions.
Proteins are long chains or polymers of a specific type of amino acid known as an alpha-amino acid. Lets see each different amino acid according to their classification. What makes each amino acid unique.
Out of the 20 amino acids 9 are the essential amino acids and the others are Non-essential amino acids. What makes amino acids unique from one another1 point A. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers.
The R group the central carbon the carbon ring the carboxyl group the amino group Question 11 1 pts Which of the following would activate a protein. The difference between amino acids with the same property is the molecular structure of their R groups and how that influences other amino acids ability to interact with them. What makes an amino acid unique is the attachment of a fourth side chain called an R group.
This means that no two amino acids posseses the same R group or side chain. Alpha-amino acids are unique because the amino and carboxylic acid functional groups are separated by only one carbon atom which is usually a chiral carbon. Even s slight change in this can alter tertiary.
Essential amino acids and Non-essential amino acids together make up the 20 amino acids. Overall three dimensional shape B. Amino acids are organic molecules that when linked together with other amino acids form a protein.
Structurally amino acids are generally composed of an amino group NH2 a carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain. All The 20 amino acids are classified into two different amino acid groups. There are about 20 amino acids in nature.
An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid. The term amino acid is short for α-amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid. Check out now the facts you probably did not know about.
They differ from each other in their side-chain called R group. Label the diagram below with the primary secondary tertiary and quaternary structures нно НН H o HH C Do the following descriptions occur in the primary secondary tertiary or quaternary structure. In this article we will solely focus on the alpha-amino acids that make up proteins.
An amino acid is an organic molecule that is made up of a basic amino group NH 2 an acidic carboxyl group COOH and an organic R group or side chain that is unique to each amino acid.

Periodic Table Of Amino Acids Biochemistry Notes Teaching Chemistry Chemistry Classroom

Amino Acids And Protein Structure Mp4 Sports Nutrition Shack Amino Acids Peptide Bond Protein
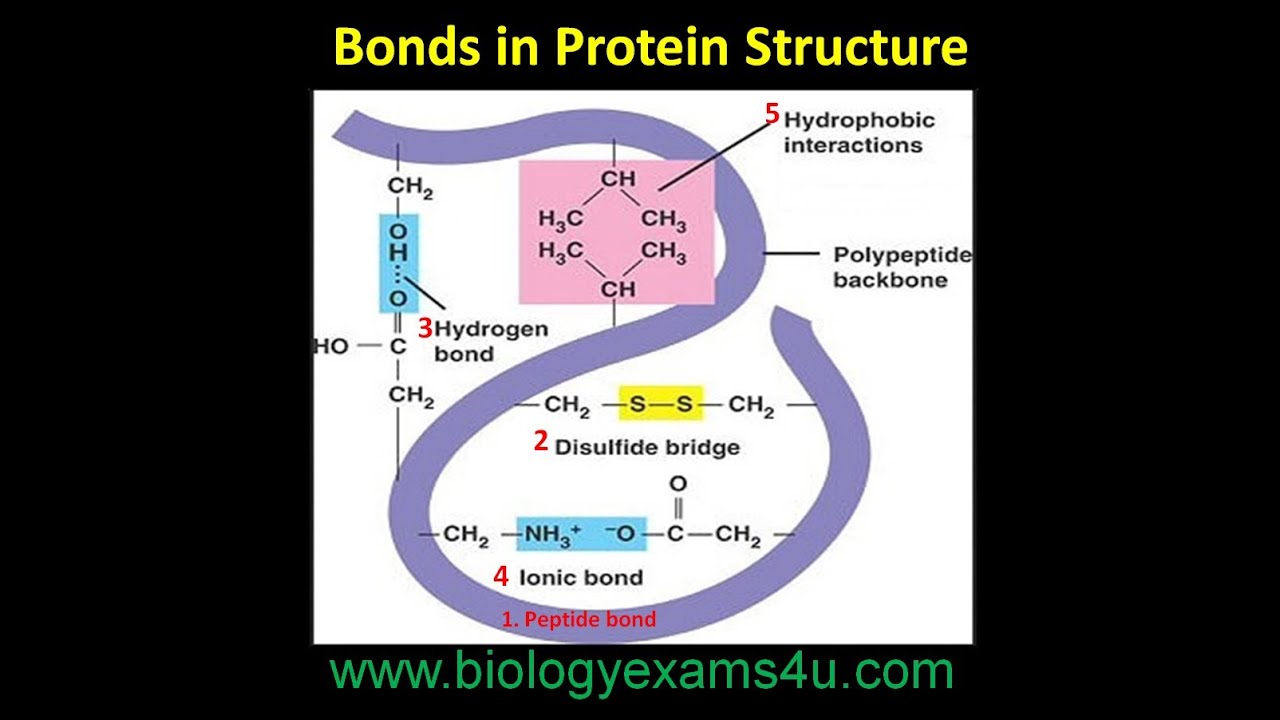
5 Types Of Bonds In Protein Structure Simplified Summary Peptide Bond Biology Lessons Biochemistry

Comments
Post a Comment